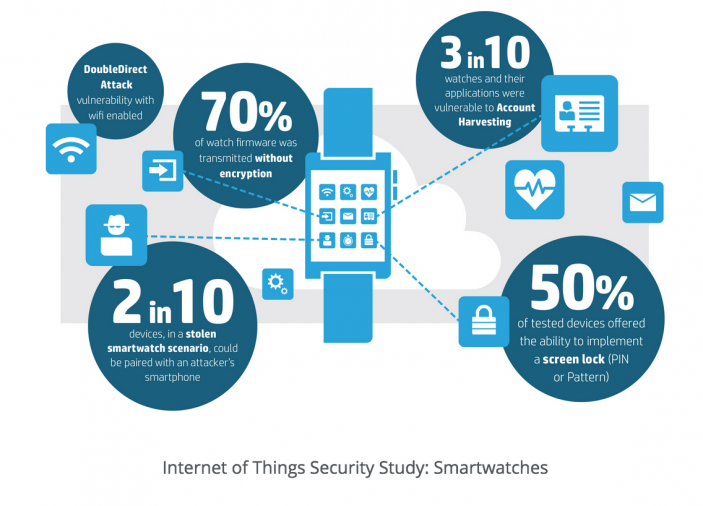
Smartwatches are a huge security risk according to a new study by Hewlett-Packard. HP tested 10 different smartwatches and found that 100% were vulnerable to cyber attacks.
The vulnerabilities include insufficient authentication, lack of encryption and privacy concerns, according to HP Fortify.
The study found, “Smartwatches with network and communication functionality represent a new and open frontier for cyber-attack.” They could be used to hack into connected cars and smart home accessories. Any device you connect to your smartwatch is vulnerable.
These flaws could allow hackers to get ahold of sensitive personal information including your health data.
“Smartwatches have only just started to become a part of our lives, but they deliver a new level of functionality that could potentially open the door to new threats to sensitive information and activities,” HP GM Jason Schmitt said.
The five most common security issues were insufficient user authentification, lack of transport encryption, insecure interfaces, insecure software/firmware and privacy concerns that include information such as name, address, date of birth, weight, gender, heart rate and other health information.
Schmitt added, “As the adoption of smartwatches accelerates, the platform will become vastly more attractive to those who would abuse that access, making it critical that we take precautions when transmitting personal data or connecting smartwatches into corporate networks.”
Researchers suggest users “do not enable sensitive access control functions such as car or home access unless strong authorization is offered. In addition, enabling passcode functionality, ensuring strong passwords and instituting two-factor authentication will help prevent unauthorized access to data.”
The smartwatches tested used both Android and iOS cloud operating systems. Researchers combined manual testing with automated tools to reach their results, according to the study.