Growing demand across mobile networks and small cell deployments from 4G and IoT set to increase need for fiber support.
Editor’s Note: With 2017 now upon us, RCR Wireless News has gathered predictions from across the mobile telecommunications space on what they expect to see in the new year.
Before the days when you could grab your phone, log onto Twitter, receive work emails or watch streaming NFL games from anywhere, the phone was just a phone. It allowed you to phone home, call your grandmother on her birthday and check voicemails at work – and the wireless networks were originally built to support this model. Voice calls were all you could expect or thought you ever needed from this type of device.
But then the model changed. Added services started with the onset of the mobile communications 2G networks, which marked the shift from voice to data and provided the services that are now a regular part of our lives today, such as text messages, picture messages and multimedia messages. The launch of 3G technology redefined the internet experience. The latest 4G network is an IP-based integrated system that is highly regarded for its ability to provide excellent quality, security and data speed. This growth trajectory for mobile multimedia services is expected to accelerate over the next decade.
But before providers can deliver exciting new wireless broadband services for virtual reality, augmented reality, video-on-demand and other services to consumers, network operators need to manage the impact of the explosive growth of data already traversing their networks. Although the data equation is well documented, the challenge of increasing data requirements is never ending and remains a top priority for service providers.
Challenging on multiple fronts, service providers must consider the mobile data traffic that comes from fixed networks, as well as faster broadband speeds which inspires increased consumption and use of high-bandwidth content and applications. The “Cisco Visual Networking Index, 2015-2020,” details the widespread impact of the processes and applications that are creating added demand. With the adoption of personal devices and deployment of machine-to-machine connections quickly lighting up networks, the amount of data impacting network traffic is at an all-time high. Advancements in the “internet of things” are continuing to drive IP traffic and tangible growth in the market. Applications such as video surveillance, smart meters, digital health monitors and a host of other M2M services are creating new network requirements and incremental traffic increases. Video services and content continues to dominate network traffic accounting for 79% of global internet traffic by 2020 – up from 63% in 2015. In 10 years, the demand for data capacity will likely be somewhere in the neighborhood of 1,000 times what it is today.
Companies are competing for capacity, driven by fiber
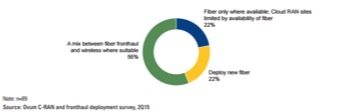
Optical fiber – whether deployed as part of a wireline telecom provider, wireline cable or wireless build – is the medium upon which data traffic is most effectively carried. The next generation of wireless technology deployments, including small cells, will require additional site data capacity, increasing the need for fiber and requiring service providers to rethink strategies. Research from IHS found the market for small cell backhaul connections is expected to grow to about 960,000 connections, up from 75,000 connections, by 2019. Although small cells promise seamless coverage, conventional backhaul techniques are being abandoned in favor of fiber. A recent Ovum survey found 44% of service providers will exclusively use fiber for centralized radio access network fronthaul, highlighting the role of fiber in nearly any scenario as service providers deploy fronthaul for CRAN environments. Essentially, wireless broadband will need substantial fiber backhaul and fronthaul equipment, making fiber management and pathway products absolutely essential to support high-speed and reliable broadband service.
The advances in wireless bandwidth performance will enable service providers to enhance the service packages they offer consumers and open new opportunities for fiber connectivity and management in a place that didn’t exist previously. We look to wireless broadband as providing mobility – while wireline broadband, or fiber directly to the home or business, provides the ultimate in productivity and quality of experience.
As network operators make significant capital investments to build out the network, provide sufficient capacity and to put in place scalable architectures to handle ever-increasing needs, they need to consider fiber management and connectivity for both wireline and wireless. The ability to deliver fiber anywhere is well-suited to addressing deployment challenges across a heterogeneous wireline and wireless landscape, whether it’s for delivering fiber to the home, business, curb, small cell antenna, remote radio head, or cell tower.

