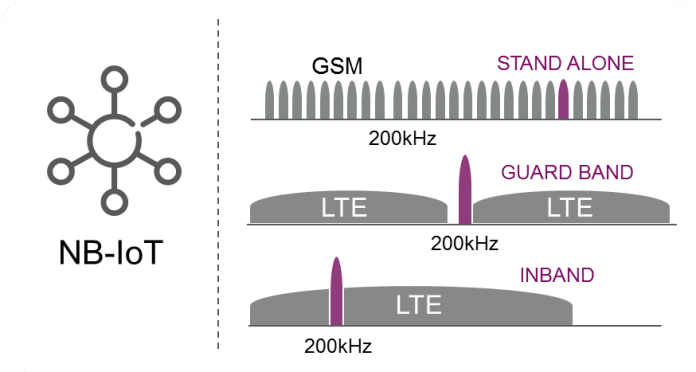
Narrowband internet of things (NB-IoT) is a standards-based low power wide area (LPWA) technology developed to enable a wide range of new IoT devices and services. Ratified by the 3GPP, a telecoms standards body which works to develop future generation wireless technologies, NB-IoT will soon be deployed by operators across the globe.
The technology was developed to enable efficient communication and long battery life for mass distributed devices across wide geographical footprints and deep within urban infrastructure. Here we describe three NB-IoT case studies.
Deutsche Telekom (Germany)
German telecoms operator Deutsche Telekom (DT) has tested LPWA-enabled smart parking services on its campus at its headquarters in Bonn. Each parking space was equipped with an ultrasonic sensor, which can detect whether the space is occupied. The sensor then used a LPWA connection to transmit the data, via a network gateway, to a server in the cloud, which then aggregated the information and made it available to drivers arriving at the campus via a smartphone app.
For the trial, the German telco used narrowband internet of things (NB-IoT) with the support of Chinese equipment vendor Huawei, which upgraded the software in existing commercial base stations to make them NB-IoT capable.
Aguas de Valencia (Spain)
Utilities around the world are installing smart meters that can monitor customers’ usage of energy or water in near real-time, cutting costs and helping to balance supply and demand. But it can be expensive and difficult to connect meters that are deep inside buildings, in basements or under manhole covers. Mobile operator Vodafone and Spanish water group Aguas de Valencia are exploring how new LPWA technologies could address this challenge.
The results of a trial in the Spanish town of Moncada suggested that LPWA networks could bring connectivity to utility meters beyond the reach of existing wireless solutions. Vodafone is testing a LPWA network in the town of Moncada. It is using LPWA connectivity to connect meters run by the water utility Aguas de Valencia. Many of the meters involved in the trial are in locations that lack conventional cellular coverage, such as basements or beneath manhole covers.
Aguas de Valencia was looking for a standardized solution that can be deployed quickly and efficiently. “Until now, meter reading technology has been proprietary and has required the installation of our own infrastructure,” said Víctor González, metering and smart reading manager, at Aguas de Valencia.
To that end, Aguas de Valencia has carried out a NB-IoT trial with Vodafone. For the trial, which began in November 2015, Vodafone and Huawei had upgraded six base stations to support NB-IoT using 900Mhz spectrum. The operator has also implemented NB-IoT technology to connect 42 meters, which have been equipped with modules supplied by Swiss firm u-blox.
Sea Mammal Research Unit (Scotland)
The University of St. Andrews Sea Mammal Research Unit (SMRU) is developing smart telemetry tags using NB-IoT technology to track and monitor the movement of harbor seals and research their population decline.
The new sensors being developed by SMRU will be harmlessly attached to the seals in order to log detailed data on the animals’ behavior, such as location and dive depth, as well as temperature, salinity and, eventually, underwater sound.
SMRU expects to trial the new NB-IoT enabled marine tags later this year. In 2016, it successfully gathered information for analysis from harbor seals in Orkney, Scotland, using machine-to-machine (M2M) technology.