Ireland has put city administrators and neutral host networks at the centre of a new five-year roadmap to bring 5G connectivity to the nation, and to stimulate economic growth. Dublin City Council will lead a “market engagement exercise” through the rest of 2020 to review the opportunity of neutral-host and shared-infrastructure 5G deployments.
Dublin City Council and Sligo County Council have teamed up with CONNECT, the country’s research centre for future networks and communications, to issue a discussion document that sets out these priorities, as a means to remove barriers to 5G rollout at local and national level. It makes clear a coordinated approach among stakeholders is the only way to deliver on the economic potential associated with 5G.
The document polled mobile operators, telecoms vendors, and city authorities. It says national and local government must be proactive and coordinated, and proposes a National Working Group to collate infrastructure assets and navigate rollout of 5G networks, for usage by the public, as well as by smart cities, enterprises, and Industry 4.0 operatives. The state-owned Electricity Supply Board (ESB) must also be closely engaged, to resolve unmetered power issues for the installation of small cells on unmetered supply.
A neutral host model, where open 5G radio infrastructure is shared by these various groups, should be followed across Ireland, it suggests. It recommends a neutral host model — available in “many flavours”, but geared so a local authority works with a facilitating entity who manages small cells affixed to city asset — over a shared infrastructure model, where multiple equipment from different operators resides on a single city asset, and an ‘exclusive concession’, where one operator gains exclusive access to city assets.
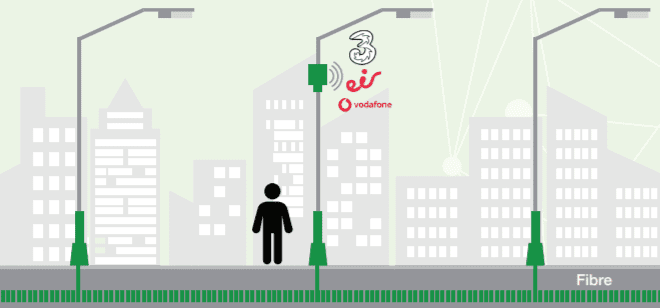
The document states: “It is an attractive model from a local authority perspective seeing that the neutral host network will rely on single equipment and devices compared to multiple such installations. This is especially true in high footfall areas of cities and towns where there is risk of limited number of assets for installation, and potential ‘visual pollution’ from too many deployments as seen in the following graphics.”
It notes: “The neutral host model also comes with additional costs and technical risks for operators which will require a lot more upskilling across the wider telecoms sector, which are likely to be offset by reduced infrastructure and maintenance costs.”
Dublin City Council has already been trialling a neutral host model in the city’s docklands, as part of a research and industry partnership between CONNECT and Dense Air, a subsidiary of network infrastructure vendor Airspan. The project is designed to hasten network densification in support of in-building connectivity, IoT implementations, wireless backhaul and boosting carrier services.
Dense Air controls its own mid-band spectrum in Ireland, as well as in Belgium, Portugal, New Zealand, and Australia. The company provides neutral host network services “designed to improve coverage and capacity in locations that are technically difficult or commercially uneconomic to support,” according to its website.
But a nationwide neutral host strategy within Irish cities and towns would require local authorities to engage with third-party operators through the development of a public/private partnership (PPP) to help fund, operate and maintain the network for ‘open access’, notes the document. “Collaboration with a third-party operator would enable local authorities to explore opportunities to generate new revenue streams from the neutral host network,” it says.
Indeed, local authorities will play an instrumental role in Ireland’s “path to 5G”, the report says, by virtue of their operational influence and ownership of assets such as poles, ducting, and street furniture in key locations.
The document states: “Local authorities and state bodies… need to be more proactive in how they can leverage their assets to support 5G. This needs to go beyond the current situation which deals with ad-hoc requests to a more structured model where the local authority facilitates access to assets in a manner which is open and transparent for operators, as well as for users, and citizens in general.”
It goes on: “Local authorities must ensure equal access to their assets considering their strategic importance, rather than reward a first come first served, or highest bidder exclusive approach, to small cell deployments. Ideally, a neutral host network can be implemented to maximise asset utilisation, and wide-spread connectivity. When there is a lack of collaboration and coordination in a process as intricate as 5G deployment, the network will fail to achieve its full potential and citizens will be left disadvantaged.”
Brendan Jennings, interim director of CONNECT, the Science Foundation Ireland research centre for future networks and communications, said: “The economic opportunity associated with 5G and next-generation networks is well documented: the global impact in goods and services is expected to reach $12 trillion by 2035. A coordinated approach will ensure that all regions in Ireland can capitalise on this.
He added: “The economic difficulties due to the COVID-19 pandemic make this more urgent. The document recommends a National Working Group to shape a shared vision for connectivity in Ireland. It should be composed of key stakeholders: government departments, local authorities, mobile operators, equipment vendors, business groups, regulators, safety experts, and the research community.
Jamie Cudden, smart city lead at Dublin City Council, said: “Local authorities, in particular, will play a vital role in Ireland’s path to 5G, so collaboration and engagement between councils and mobile operators will be essential to facilitate a sustainable rollout. For instance, the challenge of accessing power in an affordable manner is a make or break issue for future deployment of 5G.
“So it is essential that we resolve unmetered power issues for the installation of small cells on unmetered supply. There is also a need for a database of assets such as street furniture, ducting, and streetlights, and an assessment of their suitability for use in 5G deployments.”
Nigel Carter, digital innovation lead for Sligo County Council, said: “We hope the document stimulates debate and discussion among stakeholders to ensure that Ireland realises its connectivity potential and remains a highly competitive economy. In addition, it is critically important that safety monitoring continues and the latest scientific guidance from the World Health Organisation (WHO) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is communicated clearly.”

