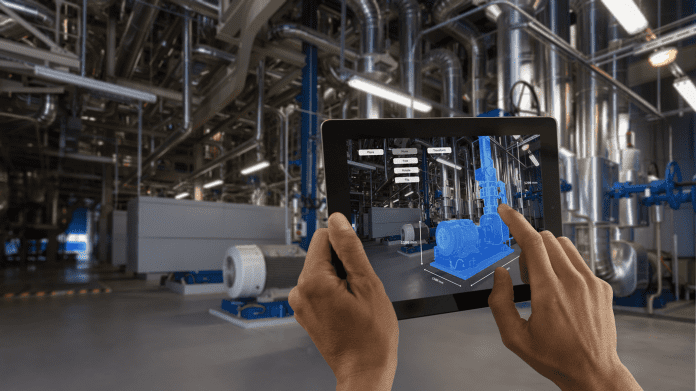
Use of digital twins among tech trends ABI sees shaping 2022
Global spending on industrial digital twins is forecasted to grow from $4.6 billion in 2022 to $33.9 billion in 2030 at a 28% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), according to a study by ABI Research.
In its new whitepaper, dubbed ‘70 Technology Trends That Will—and Will Not—Shape 2022’, ABI Research noted that manufacturers need a range of capabilities to deploy digital twins, including Computer-Aided Design (CAD) modeling, connectivity, cloud computing, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) software platforms, remote monitoring, hardware for shop floor workers (tablets, AR glasses), physics-based simulation, ML, and systems integration. “This is because digital twins are not a technology, but a composition of solutions aimed at bridging the physical and digital worlds, from design through simulation, manufacturing, assembly, and after-sales service and support.”
“Over the last few years, digital twins have grown from a concept to become mainstream with the help of IIoT dashboards and near-real-time reporting. This level of maturity has been accompanied by new thought constructs, such as the use and implementation of AI at scale, changing requirements like the need for model libraries and standards bodies, and soon, the emergence of digital twin marketplaces that enable Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) and other third parties to build relevant tools for the ecosystem. These tools are essential for continued value creation and the wider democratization and adoption of digital twins,” ABI Research said.
The whitepaper also highlighted that suppliers of industrial applications, such as simulation software and product life cycle management, are moving from providing only on-premises solutions and are making their solutions available via the cloud and offered on a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) basis. “Suppliers will emphasize the ability to work on projects regardless of location and the capability to ensure traceability of design changes to deliver a digital thread across teams, but also so that customers can open the solutions to collaborate with their technology partners and suppliers on designs. In theory, the extension of the digital thread to outsiders will accelerate innovation cycles and identify issues earlier; however, to protect their IP, customers will need to think carefully about guardrails regarding who is gaining access and traceability surrounding their activities.”
The consultancy firm also noted that 5G will not permeate the production line in 2022. As of July 2021, there were 84 sites with publicly announced private cellular network (4G/5G) deployments. All are at large companies and facilities, with examples including ABB, Airbus, BASF, Daimler AG, Ford, Haier, Konecranes, and Nippon Steel. “While important, current deployments are mostly used as campus networks or in a lab or intermediary production development center for non-industrial production applications. Standards work by 3GPP and 5G-ACIA continues to advance adoption and use of the technology; however, the device ecosystem and implementation/management functions lag.” The whitepaper also highlighted that there is also a question of relevance as two-thirds of manufacturers employ fewer than 20 people. In its current form, working with and trialing 5G in manufacturing favors large companies/factories with the R&D capital to test and learn. “These larger companies and locations have started to evaluate the cost and benefits of different deployment scenarios. However, 5G will not be relied upon for production critical applications at scale until 2024.”