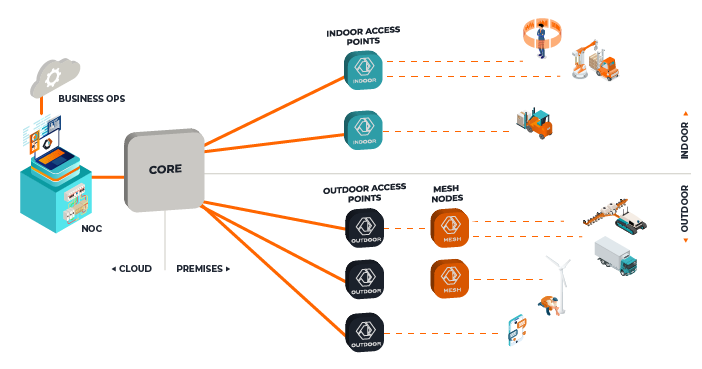
For many enterprises, Wi-Fi is the go-to infrastructure for connectivity. It is a vital and essential component for supporting the full gamut of business services and applications that employees and visitors rely upon. While Wi-Fi works perfectly well in office settings, or for transporting low-latency applications like email or IoT data, many businesses also use it to support a new generation of applications that require high bandwidth, low latency, and robust security, such as AR/VR/XR tools and rich media. In addition, while Wi-Fi is more than adequate to cover offices, it can be expensive and complicated to deploy in larger footprints such as warehouses, manufacturing plants, farms, stadiums, and transportation hubs. In these instances, the Wi-Fi network, in essence, becomes a ‘catch-all’ that works, but is not particularly suited to comfortably and economically handle the escalating traffic that is generated in non-office settings.
Enterprises should examine the viability of placing high-performance and mission-critical services on a private cellular network to augment their Wi-Fi networks. It provides a flexible and cost-efficient strategy that can ensure reliable network coverage, particularly as business needs evolve. Furthermore, employing mesh technologies in the private cellular network extends both economic and performance advantages.
Where is Mesh Best?
Before discussing mesh, it is important to understand how radio bandwidth is utilized in a typical wireless network—both Wi-Fi and cellular. Endpoint devices, whether a phone, computer, scanner, or robot, connect wirelessly to the access point (AP) with the strongest signal. In a traditional network configuration, an AP has a wired backhaul connection to the network uplink. When these physical connection points are not available or cost effective to install, wireless mesh connectivity can be the answer.
A mesh network can reduce or eliminate cabled uplink connections by utilizing some of its bandwidth for backhaul and relayed connection to additional APs. This traditionally causes inefficient bandwidth use, which may be acceptable when data demands are low and spectrum is free, but when network demand inevitably increases or the spectrum is licensed, this inefficiency can be costly and result in degraded performance.
A more efficient mesh solution utilizes the full bidirectional bandwidth for both backhaul and frontside delivery through the application of advanced technologies, such as dynamic interference cancellation and micro-second scheduling of transmit and receive functions, which can double the data capacity in each node and provide as much as a 10x performance improvement in the network. The efficiency of the mesh also minimizes latency and reduces signal jitter to assure reliable service delivery.
In addition to improving bandwidth utilization, private cellular mesh networks are highly reliable, with the inherent capability to hand off devices between nodes and automatically adjust to node failures or delays, thereby enabling cellular edge devices to connect to the next strongest access point on the fly.
More Advantages of Private Cellular Mesh
Extend, don’t replace. Cellular mesh provides a fully compatible and cost-effective way to extend the physical wireless coverage boundaries of enterprise infrastructure with increased control, security, and performance, and at lower installation and operational costs.
Due to the operating frequencies and relative transmit power and receiving sensitivity, coverage area via private cellular mesh will require one-fourth the APs indoors and one-twentieth for outdoor implementations. Fewer APs means lower costs for installation, power, and maintenance.
The security design of cellular technology also severely limits wireless network intrusion vectors and virtually eliminates the man-in-the-middle and interception attack vulnerabilities of long-range Wi-Fi systems.
Conclusion
Private cellular mesh networks provide a strategy to complement Wi-Fi in ways that improve the performance, reliability, bandwidth efficiency, and security requirements needed for crucial business applications. It is the perfect choice for any enterprise that relies on mission-critical applications and services in industrial, agriculture, warehouse, and campus settings.