MWC Shanghai 2023 is set to return this June to the Shanghai New International Expo Center. After the success of MWC Shanghai 2021, which saw more than 200,000 attendees from 114 countries and territories, there has been high anticipation for the return of the event this year, which will host keynote presentations from leaders in the telecommunication industry and showcase advanced technology demonstrations from various innovators.
There is little doubt as to why China remains a very suitable location to host MWC in the Asia-Pacific region. Since the official commencement of 5G in China in June 2019, China has established itself as one of the global leaders in 5G deployments, innovations and commercialization. The four major operators in China — China Telecom, China Mobile, China Unicom and China Broadnet — have been critical proponents in driving the rollout and adoption of 5G services across consumers and businesses nationwide.
5G growth at breakneck speed
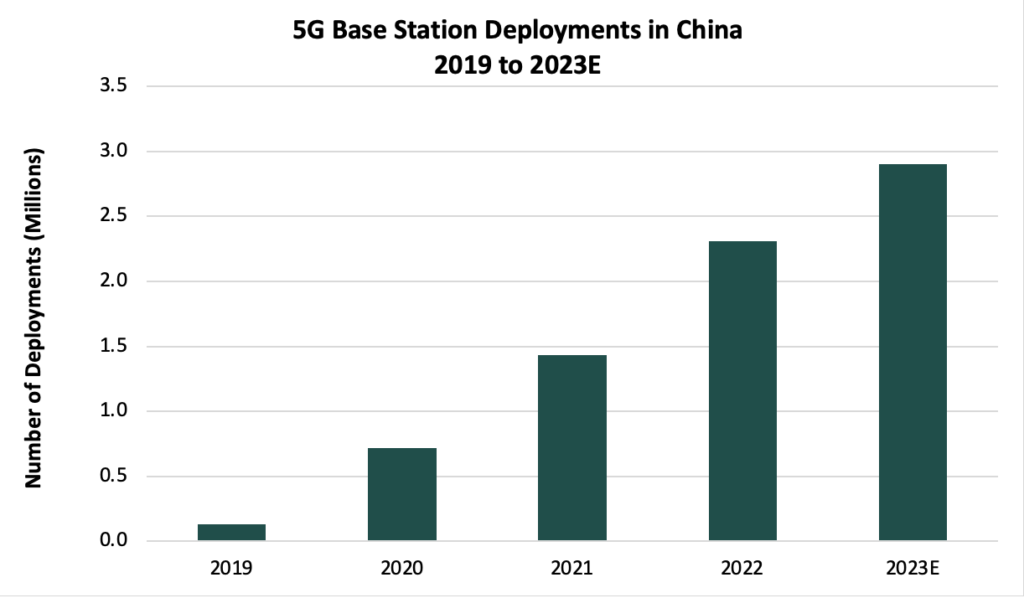
As of April 2023, the country has built or upgraded more than 2.7 million 5G base stations — accounting for 24.5% of the overall mobile base stations nationwide — and looks likely to meet or even exceed the initial target of 2.9 million deployed 5G base stations by the end of 2023 made by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT).
The operators’ rapid rollouts of 5G networks have also seen high adoption rates of 5G subscription plans among consumers. By the end of 1Q 2023, the number of 5G subscribers in the country increased to around 1.2 billion, which is an increase of more than 40% from approximately 850 million 5G subscribers as of March 2022. 5G subscription penetration rates were above 60% across all operators.
In terms of revenue, China Mobile reported an 8.1% Year-over-Year (YoY) increase in telecommunication service revenue, with mobile Average Revenue per User (ARPU) up 0.4% to CNY49 (US$6.9). China Telecom also reported a 3.7% YoY increase in mobile communications service revenue with mobile ARPU up 0.4% to CNY45.2 (US$6.3), whereas China Unicom saw a 3-year consecutive growth in mobile ARPU to CNY44.3 (US$6.2).
In the enterprise sector, the three operators have collectively reached a cumulative total of more than 49,000 5G commercial projects as of the end of 2022, with China’s MIIT reporting that the operators have built more than 6,000 5G private networks, to date.
Coordinated and sustained network investment
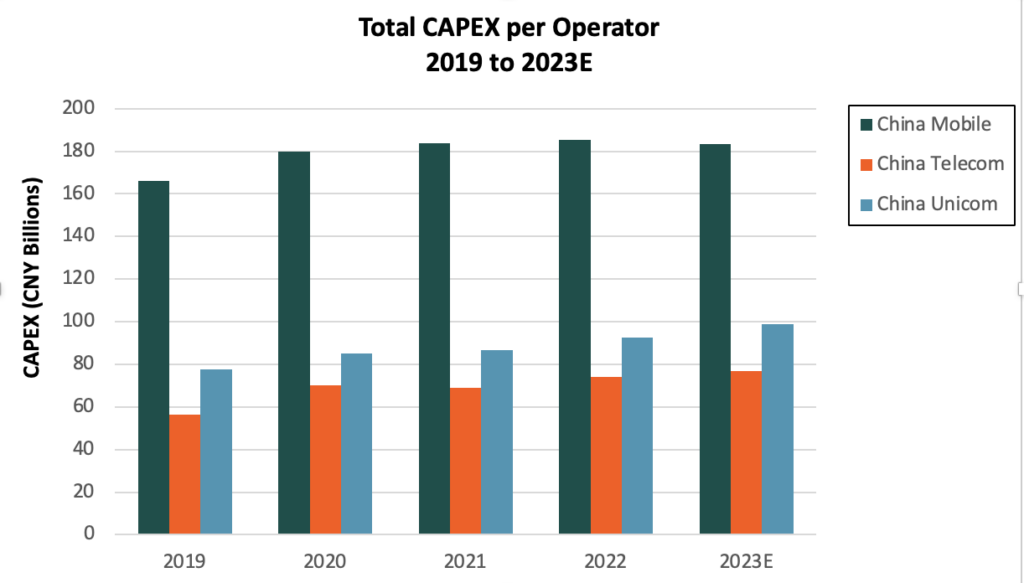
At the heart of China’s 5G strategy is coordinated and sustained network investment from its operators. To date, the Chinese operators have invested an accumulated CNY1.3 trillion (US$181.7 billion) in total Capital Expenditure (CAPEX between 2019 and 2022, with more than CNY530 billion (US$74.2 billion) of that going into 5G-related CAPEX. This has enabled the rapid rollout of 5G Standalone (SA) networks that has supported enhanced 5G user experiences. This is made evident by Ookla’s Speedtest, which indicated higher than 250 Megabits per Second (Mbps) 5G median download speeds across China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom in 1Q 2023.
Despite the already extensive deployment of 5G networks across the nation, Chinese operators have indicated their plans to continue heavily investing in their networks in 2023. For example, China Mobile has announced its plans to invest approximately CNY83 billion (US$11.6 billion) in terms of CAPEX in 2023. As part of this CAPEX, China Mobile is looking to procure more than 412,000 5G base stations between 2023 and 2024. Separately, China Telecom has announced its plans to spend CNY31.5 billion (US$4.4 billion) on expanding its mobile networks, with a target to deploy more than 1.2 million 5G base stations by the end of 2023.
New 5G business models and revenue streams
Chinese operators have leveraged the different capabilities of 5G to uncover new business models and revenue streams beyond traditional connectivity services. For example, China Mobile has moved into the digital content market with its “Migu service,” which offers video content, cloud games and other premium Internet products, as well as moving into the Financial Technology (FinTech) segment. China Telecom has invested in its cloud services portfolio, with revenue from the China Telecom Cloud increasing by 107.5% YoY to reach CNY57.9 billion (US$8.1 billion) in 2022. Cloud and Internet of Things (IoT) services were large sources of growth for China Unicom, with revenue growing 121% YoY to CNY36.1 billion (US$5.1 billion) and 42% YoY to CNY8.6 billion (US$1.2 billion), respectively.
Fostering 5G industry alliances
The four mobile operators have also worked closely with partners from diverse industry verticals — mines, factories, logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, marine ports, media, energy, agriculture, etc. — as well as equipment vendors to develop customized innovative 5G applications.
In the logistics sector, for example, China Mobile Zhejiang and a group of partners worked with the Ningbo-Zhoushan Port operator, Zhejiang Seaport Investment and Operations Group, to implement a 5G network solution that enabled real-time asset inspection and tracking, remote operations of Rubber-Tired Gantries (RTGs) and automation of container truck fleets through low-latency communications. In the manufacturing field, Baosteel Zhanjiang Iron and Steel partnered with China Unicom to deploy a private industrial 5G network for use cases, such as real-time online monitoring of operations, Augmented Reality (AR) assistance and 5G-connected inspection robots.
Upgrade program that supports service innovation
Investment in the next evolution of 5G in China is very much underway. In March 2023, China Mobile Hangzhou and Huawei demonstrated a 5G-Advanced deployment, achieving peak rates of over 10 Gigabits per Second (Gbps) data rates. Furthermore, China Mobile announced the launch of its “Dual 10 Gigabit City” project in Hangzhou in June 2023, which aims to leverage 5G-Advanced technology to enable the city’s next-generation digital economy. As a key first use case, the project aims to make available “glasses-free,” Three-Dimensional (3D) live-streaming of the upcoming Asian Games — held in the city of Hangzhou — to viewers.
Insights for other markets
China can show the world a blueprint of how 5G networks can be scaled effectively with high commercialization value. In the face of strong global economic headwinds, operators worldwide need to consider how they can maximize Returns on Investment (ROIs) from their 5G investments. ABI Research has distilled the lessons that other operators can learn into two key points:
- The need for prudent and committed investments: To ensure that customers are able to enjoy the full range of benefits and capabilities supported by 5G, operators will need to be committed to not only build out their 5G networks, but eventually to also transition to 5G SA networks. In the early stages, 5G SA deployments could be done in a phased approach, targeting key cities with stronger demand and need for 5G capabilities.
- The Need to create strong industry partnerships and robust vendor ecosystems to spur 5G commercialization opportunities: Beyond connectivity, operators need to consider how they can partner with industry players to provide new consumer services, such as high-quality digital content and customized enterprise solutions that leverage the high data speeds and low latencies provided by 5G.
With China already building up speed toward 5G-Advanced deployments, there are certainly insights that operators in other countries can gain from the Chinese market. With each cellular generation (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, etc.), the benefits for the end user, commercial enterprise and society are only continuing to multiply.
*Conversions from CNY to US$ are based on prevailing currency exchange rates where 1CNY = US$0.14