The global cellular IoT market remains impacted by challenges with inventory and demand – except in China and India, where continued growth in sales of cellular meters and trackers, plus other devices, sent the overall IoT module market spiralling upwards by seven percent in the first quarter of 2024. The result, sparked by demand in China and India, shows the cellular IoT market is exhibiting “early signs of recovery” overall, compared with a year-ago, said Counterpoint Research.
It suggested the market overall will reassert its buoyancy next year (2025), as LTE-based Cat 1 bis continues to reduce in price and gain share from NB-IoT and Cat 1 technologies, and, notably, as reduced capability 5G (RedCap) IoT modules enter the market in more serious volume – and as China subsidises their takeup. 4G Cat 1 bis captured one-third of cellular IoT module sales in the first quarter. It said IoT module shipments will grow at a compound annual rate (CAGR) of nine percent between 2023 and 2030.
Counterpoint Research commented: “There is a technology transition underway [currently] in China with Cat 1 bis gaining share… [From 2025] subsidies… will drive the adoption of 5G [RedCap] in the IoT module market.”
But for now, the broader cellular IoT industry remains hobbled by long-Covid, said the firm, even as supply has started to chime with patchy demand. Excluding sales in China, the global market saw a decline of two percent year-on-year – “due to low demand and inventory buildup at the customer end”, said Counterpoint Research. Chinese module maker Quectel remains the biggest brand in the space, inside and outside of China – by an astonishing margin, with 38.7 and 37.1 percent of sales in the quarter, respectively.
No other module maker got near (see graphic); Telit Cinterion, the one non-Chinese brand among the leading suppliers, registered in sixth place in the global rankings with 4.8 percent of the total market, and in second outside of its main rivals’ home country with 12.2 percent of non-China sales. Overall, Fibocom (6.9 percent), China Mobile (6.8 percent), SIMcom (5.7 percent), and Neoway (also 4.8 percent) all ranked higher. Outside of China, Semtech crept into fourth with 5.7 percent of rest-of-world sales.
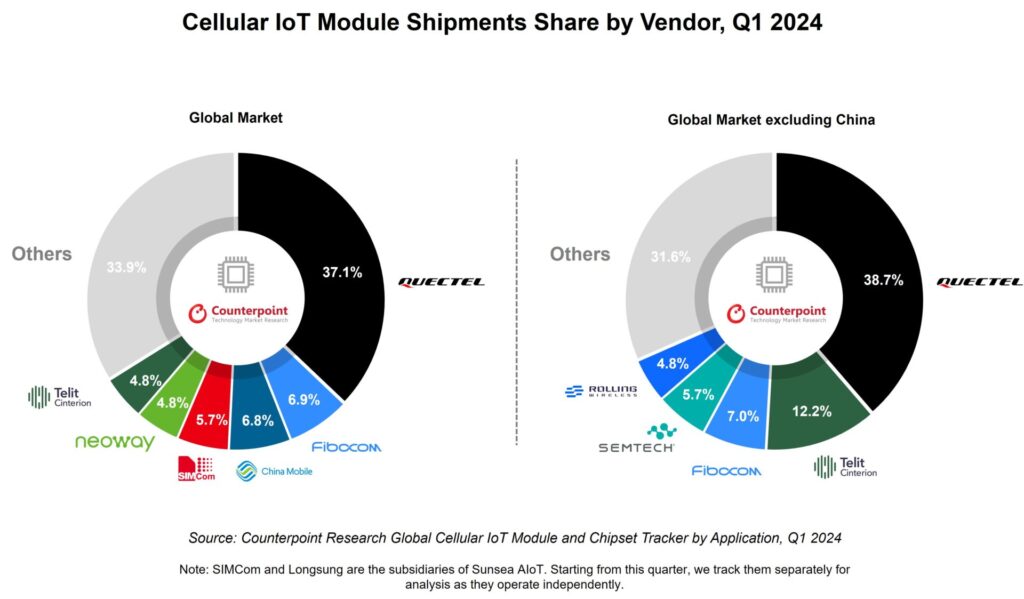
Quectel, Fibocom, and China Mobile held a 50 percent global share in the quarter. Telit Cinterion’s non-China placement was one higher than previously, said Counterpoint Research. Meanwhile, Fibocom claimed “impressive growth” with a “new high for a quarterly shipment”. “Its presence in the router/CPE and telematics segments helped [it] enter the top-three list for the international market excluding China,” it said. China Mobile saw double-digit growth; Neoway, Lierda, and Unionman have all “grown significantly “.
Mohit Agrawal, associate director at Counterpoint Research, commented: “China and India registered positive growth driven by [sales of]… smart meters, POS [devices], asset trackers, and router/CPE [devices]… Demand for cellular IoT in applications such as smart utilities, router/CPE, automotive, and asset tracking remained healthy during the quarter. However, the demand for cellular modules across retail, healthcare and industrial verticals continued to remain subdued.”
Hanumant Pawar, research analyst at the firm, said: “The market is expected to partially recover by the second half of this year with normalizing inventory levels following an improved demand situation. [It will] rebound completely by 2025, complemented by the widespread adoption of affordable 5G RedCap modules, especially in China… IoT module shipments will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of nine percent between 2023 and 2030.” The new research tracks 1,500-oddIoT module SKUs on a quarterly basis; the latest quarterly stats are available here.

