In case you missed it, California-based private 5G specialist Celona delivered a highly-engaging presentation to a highly-engaged audience at Industrial 5G Forum earlier this month – which prompted more questions than we could handle. Having presented for 20 minutes about ‘private 5G in and out of the factory’, Mehmet Yavuz, co-founder and chief technology officer at Celona, took a shot at a couple, before being rushed off ‘stage’ by RCR Wireless in order to stick to the busy event schedule. Lots of the questions went completely unanswered. As such, and as promised at the end of the session, RCR Wireless went back to Celona, and to Yavuz, to get him to write answers to all the questions we missed. Here they are; all the quotes are from Yavuz.

1 | How does Celona see the private 5G market overall? Is proper scale starting to happen, beyond just early adopters? Is new customer growth coming as fast? Or is it more about expanding existing deployments to new workloads / venues?
“Celona believes that we are ’crossing the chasm’ (Geoffrey Moore’s framework) from ‘early adopters’ to the ‘early majority’ in private 5G deployments. We are seeing a significant uptick in deployments globally, specifically in oil and gas, petrochemicals, manufacturing, and distribution centres/warehouses. Many of our [Forbes-listed] Global 2000 customers are going from PoC (proof-of-concept) to full-site to multi-site deployments. In addition to the number of new deployments, we are also seeing a growth in use cases at existing deployments including connected worker, AGV/AMR connectivity, predictive maintenance, manufacturing automation, video surveillance, and more.”
2 | How is Celona different from other private networks vendors? How does Celona differentiate itself from legacy cellular vendors like Ericsson and Nokia – and also from IT vendors like Cisco and HPE (Athonet), and OT vendors like Siemens?
“From a competition standpoint, we see them as two broad categories: multi-vendor solutions that need to be stitched together, or end-to-end turnkey solutions.
“For multi-vendor solutions (HPE / Athonet, Siemens etc ), [the] radios (RAN), core and orchestration / management systems come from multiple vendors. All these components need to be integrated together, typically by an SI (system integrator). The integration complexity and support challenges increase manifold, often leading to poor customer experience due to lack of single point of ownership and longer times to resolve issues. Furthermore, customers need a swath of skills to manage and administer their own network or depend on a managed service provider.
“On the other hand Celona 5G LAN offers a turnkey solution with radios, core, SIMs/eSIMs, and orchestration platforms that have been developed in-house, allowing seamless operation with each other: a single-pane dashboard to manage devices, network and subscribers; a single point of contact for troubleshooting the network; orchestrator tools for customers to manage their own network if they choose to.
“While legacy cellular vendors also offer turnkey solutions, those solutions are still very complex macro-network solutions that have been originally designed for [traditional] network operators and have been poorly adapted to enterprises’ requirements. These networks tend to stay separate from enterprises’ existing local-area networks. Furthermore, they provide very limited network visibility, requiring dedicated routing infrastructure, firewalls, and security policies [which are] not consistent with the rest of the enterprise [network].
“Celona 5G LAN on the other hand is built for the enterprise and integrates directly into existing LAN and routing infrastructure, offering enterprises complete control of security policies. It also integrates into existing firewalls [and] NAC services, similar to enterprise Wi-Fi networks.”
3 | How does the cost of private 5G networks / APs compare to the cost of Wi-Fi networks / APs?
“Here is an actual example comparing Wi-Fi and private LTE deployments. For the number of APs: Celona private 5G networks typically require 1/5 to 1/10 of the number of Wi-Fi APs (radios) in indoor deployments and as low as 1/30th the number of Wi-Fi APs in outdoor deployments. For installation costs: the costs, (including cable) and switch equipment, are typically much higher for Wi-Fi networks due to a much higher number of APs.
“Iit is assumed that the indoor installation is $2,500 per AP and outdoor installation is $5,000 per AP – both for private 5G and Wi-Fi networks. Note that for many industrial enterprises the installation cost may be much higher – to install an outdoor AP can be as high as $35,000 per AP. The analysis below shows a real-life example of a manufacturing floor and yard. Celona’s private 5G solution results in significantly lower TCO (total cost of ownership) compared to Wi-Fi or competitive private 5G solutions.”
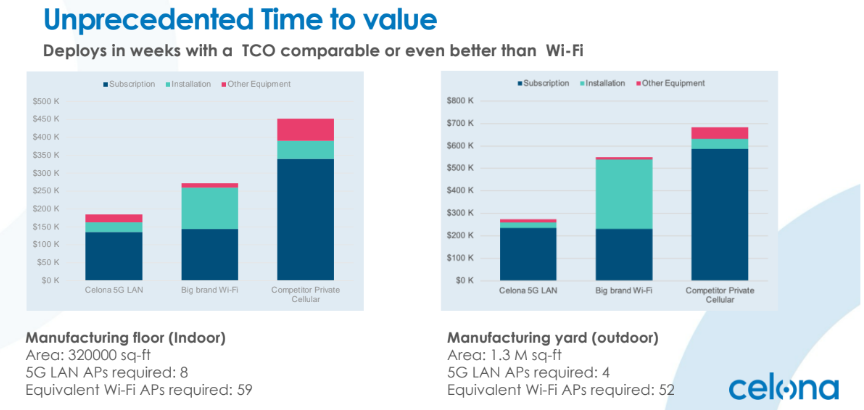
See more about comparing Wi-Fi and private wireless in a distribution centre, and a private wireless case study for manufacturing with Del Conca.
4 | What Wi-Fi standard did you base your [coverage] comparison on – to deliver equivalent coverage with five-times fewer private 5G APs?
“The Wi-Fi 6 standard was used for comparison.”
5 | Should the warehouse owner / site landlord be a part of the conversation, and contribute to the cost of a private 5G installation?
“The site owner / landlord typically needs to be involved due to equipment installation and cabling needed. We are seeing new business models emerge for warehouse owners where they are able to provide a multi-tenant private 5G infrastructure as a new revenue opportunity.”
6 | Which 3GPP release does your private 5G solution support, today?
“Celona 5G LAN currently supports 3GPP Rel 15; our upcoming solution in 2025 will support Rel 16/17/18 features.”
7 | What frequency bands does your private 5G solution support? How do you ensure seamless coverage if different frequency bands are used – such as CBRS+LAA?
“Celona private 5G RAN currently supports Bands n48, n78, n77, n79. Our upcoming solution in 2025 will support a wide frequency range from 450 MHz up to 6 GHz. RF design and automated SON considers the specific frequency channels used by the radios to ensure seamless coverage.”
8 | What are your thoughts on the long-term future of CBRS? Will its current spectrum position remain stable, or do you see changes on the horizon – especially given ongoing challenges with spectrum availability for MNOs, and the proximity of CBRS to the C-band?
“The CBRS ecosystem has been developing successfully over the last five-plus years. According to the OnGo Alliance, there are more than 400,000 CBSDs already deployed to date and operating successfully using the SAS framework. We also see increased momentum in the deployment of new private 5G networks by many customers across different verticals.
“Furthermore, we don’t see any noticeable issues with interference from adjacent bands (such as the C-Band) because proper interference avoidance mechanisms are already in place.
“Also, recent advancements as part of CBRS 2.0 improved the spectrum availability for CBRS networks further. In fact, the recent NPRM issued by FCC in August 2024 notes: ‘Commission staff have continued to work with federal partners to develop and implement refinements to improve and expand spectrum access in the 3.5 GHz band. This notice of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) is a continuation of these efforts’.
“In summary we expect CBRS spectrum usage by current and upcoming private 5G deployments in the US.”
9 | Are you offering cloud or local private 5G network management?
“Celona Orchestrator is a cloud-based solution hosted in virtual private cloud (VPC) as an isolated environment meeting strict security requirements. Note that none of the actual data traffic from a private 5G network goes to the orchestrator, and only metadata and performance metrics are used by the orchestrator for performance monitoring.”
10 | Do you support real voice services – VoLTE/VoNR (IMS) – in your solution?
“Our neutral host solution supports VoLTE / VoNR with IMS services provided by the MNOs. As part of our private 5G offering we do not provide IMS services since for private 5G networks – our customers prefer VoIP services.”
11 | What experiences have you encountered so far with eSIM – in terms of its reliability, ease of implementation, and so on?
“eSIMs are widely used by our customers for devices operating in private 5G networks. We see a lot of benefits with eSIMs – in terms of higher-level security, reliability, and management. We have been leading the industry in support of eSIMs for private 5G networks by incorporating with multiple MDM solutions (JAMF, VMware, Workspace ONE, and others) and our customers can provision eSIMs in bulk on a fleet of devices making device onboarding extremely easy.”
See more about Celona’s Aerloc integration with eSIM/MDM.
12 | Do you support ‘roaming’ of connected assets and tools from one factory to another? Once you bootstrap a device in a factory, to connect in that factory, can it also connect in other factories in other countries – where your solution is and isn’t available?
“Yes, we enable roaming of devices from one factory / site to another factory / site. In fact through the orchestrator [platform], each device or groups of devices can be authorised to operate on a single site or multiple sites.”
13 | One of the concerns for private 5G providers is that, in order to provide voice, you need IMS registration. After that, I understand that you must also provide for E911 and CALEA lawful intercept. [So] how can you offer [public 4G/5G roaming] coverage from T-Mobile and AT&T?
“As part of our neutral host offering, the traffic from mobile devices with MNO SIMs connected to the network are routed through an IPSec tunnel (through Celona MOCN Gateway) directly to [an] operator core. So, all the IMS, e911 and regulatory services are offered through the MNO core network. As a result, our neutral host offer (coverage from T-Mobile or AT&T) meets all the regulatory requirements including e911, WPS, WEA, and so on.
“Note that if our customers prefer to also get a private 5G service from the same network, the traffic from mobile devices with the private SIMs is routed to Celona Edge which provides 4G EPC and 5GC functions to those devices.”
14 | Talk about neutral-host as a gateway to private 5G – something Celona has talked about for years. Has this become a real draw for enterprises, lately? Why? Where?
“We look at the enterprise world uncarpeted / industrial spaces (refineries, manufacturing sites, warehouses, yards, and so on) and carpeted spaces (healthcare, education, and so on). While private cellular has been a primary draw for uncarpeted / industrial enterprises, neutral host has been the primary draw for the carpeted space. Now we see an inflection point for neutral host deployments since we went from just a single MNO (T-Mobile) to two MNOs (T-Mobile and AT&T). With the participation of T-Mobile and AT&T, we see a lot of interest for neutral host deployments.
“Also, for many uncarpeted / industrial enterprises, once the primary use case has been satisfied with private cellular, customers are looking for alternate ways to use the installed infrastructure for improving public cellular coverage. Celona has made it easy by offering an a-la-carte subscription offering where customers can start with either private cellular or neutral host, and then add on the other later through a simple software upgrade on the same infrastructure.”
15 | How does an IT-centric company approach the OT market? Because specifically, in terms of security (Aerloc), you talk more like Siemens (and Nokia), which always presents the OT story as the key part.
“Our customers are taking us there. Most of our customers start their private 5G deployments with connectivity for their IT devices – tablets, scanners, and so on. Over time, the reliability and mobility benefits of private wireless prompts OT use cases such as building reconfigurable assembly lines, deploying AGVs/AMRs, machine vision, and more. Adding wireless infrastructure to OT amplifies IT/OT convergence issues such as ZTNA for OT, poor integrations into firewalls and inadequate security policy enforcement.
“Celona has been working closely with customers, understanding their needs and building solutions to address these specific issues and unified them under the Celona Aerloc architecture, which is well positioned to take on these challenges.”
See more about Celona’s Aerloc solution.
16 | Can you guarantee that customer data does not leave the customer premises in each country – so sensitive data stays in the country and abides with local regulations?
“We always ensure that we meet the country and regional regulatory and data sovereignty requirements. Our customers have full control of their user data traffic and how it is routed. Lastly, Celona Orchestrator can be hosted in the specific region of interest in local AWS or GCP instances if required by the customer.”
17 | Can you talk about segregation of OT and IT data for enhanced security – in your Aerloc air-gap solution? Talk about the microslicing feature in Aerloc on different spectrum blocs – and how that supports separate IT/OT functions.
“Our MicroSlicing feature enables full segmentation of traffic into different VLAN and physical separation of IT/OT traffic on the Celona Edge.”
See more details about Celona’s MicroSlicing QoS solution for business-critical apps.
18 | What are the biggest challenges / hurdles for private 5G to go mass-market in Industry 4.0?
“We see an increased level of private 5G adoption in the market. To [make it] mass-market, the biggest challenge is the awareness of end customers. Many times, we find out that potential customers may have heard about private 5G or may have even tried a private 5G solution that did not meet their requirements. Typically, those customers may not be aware of Celona’s solution – which can fully integrate with the [their existing] LAN and meet the security and operations requirements. So, our biggest challenge is market education about our own solution.
“Another area of improvement for mass-market adoption is the widespread availability of devices with 5G support. We are very excited about the ever-increasing number of devices supporting 5G from low-end sensors to high-end compute devices. Through our device certification program, we are building partnerships with device manufacturers like Apple, Zebra, Digi, Sierra Wireless, and Honeywell to test interoperability and network performance, and ensure interoperability ahead of customer deployments.”


