Wireless Internet Service Providers (WISPs) provide high-speed connectivity to business and residential customers around the world. WISPs typically serve their local community and may extend to regional or even national network footprints. WISPs provide reliable streaming video, data, voice and IT services in a competitive market to their enterprise and residential customers. For the second year in a row, Cambium Networks, which supplies technology to the global WISP market, has conducted a vendor-neutral survey, collecting insights from 721 WISPs located in 47 countries, on 38 questions. In 2017, 514 WISPs from 37 countries responded to the vendor neutral survey of the industry. As more devices proliferate, it is clear to see that service providers play a key role in connecting people.
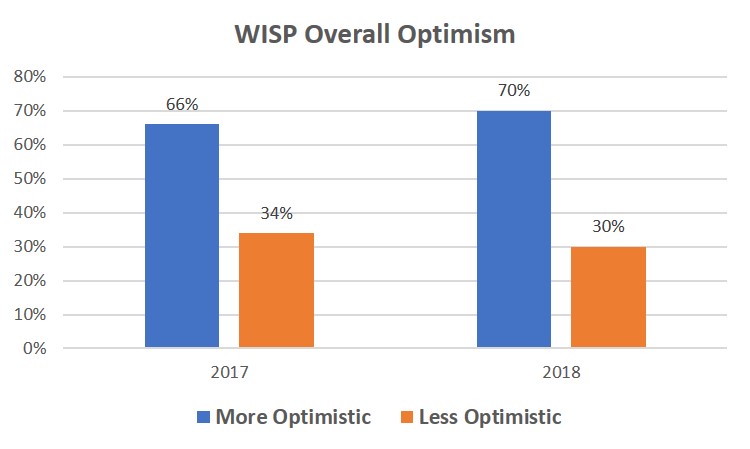
The survey’s most notable finding is the optimism that WISPs have regarding their future. When asked if they are more or less optimistic about the overall WISP business compared to last year, in 2017 66% of respondents were more optimistic, and in 2018 70% expressed more optimism.
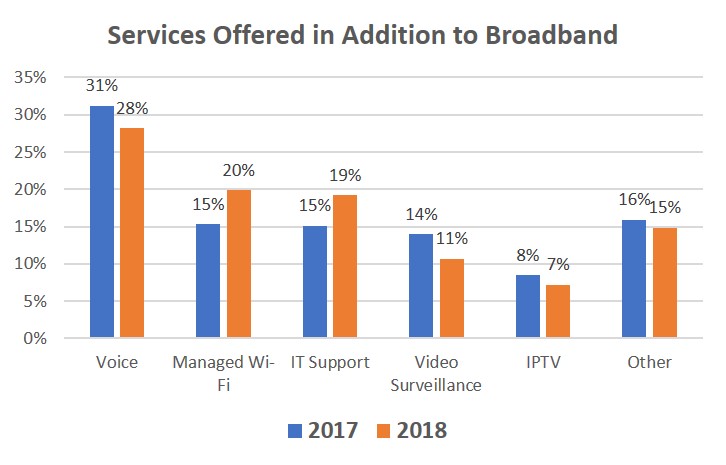
In addition to providing broadband connectivity, WISPs are finding business success in leveraging their skills to provide additional services, particularly to business customers.
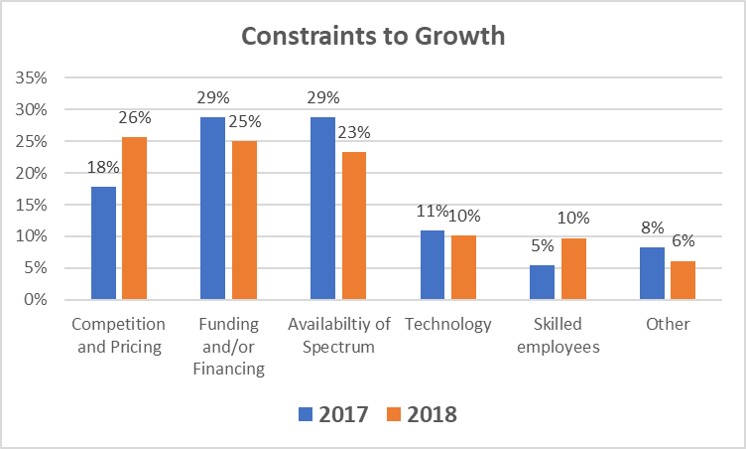
When asked what are the most significant constraints to growth, in both 2017 and 2018 availability of spectrum and funding or financing led the responses, but in 2018 competition and pricing rose to rank equally high. This indicates that WISPs are sensing competition but are optimistic that they can effectively compete and win.
LTE deployment is frequently in the news, with many large carriers making announcements of their deployments. When asked if they intend to deploy Fixed LTE in 2019, 64% of WISPs responded that they do not plan to deploy the technology this year, with 36% considering the technology.
Customers are satisfied with the service quality and the value received from WISPs. End customers demand reliable service at affordable prices and are generally indifferent to the underlying technology used to provide connectivity.
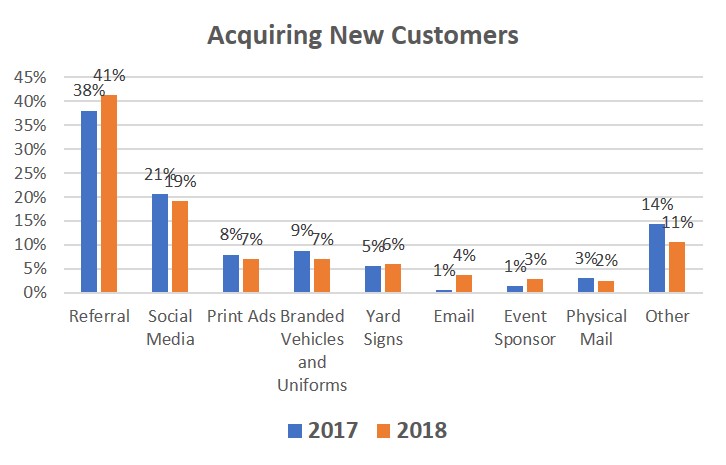
Being a local service provider confident in their ability to compete on quality of service and price, WISPs find that their most effective method to acquire new customers is through references of satisfied subscribers.
Additional Findings from the 2018 Survey:
Technology:
- 75% use fixed wireless broadband as their primary technology
- 75% primarily use the 5 GHz unlicensed frequency band
- 66% use unlicensed frequencies for backhaul
- 66% are also using fiber somewhere in their network
- 64% have no plans to deploy LTE in 2019; they do feel that the most important driving factor for LTE is better coverage
- 40% report that reliable connectivity is the most important aspect when selecting equipment
Markets
- There is a relatively even distribution between WISPs which serve rural, suburban and urban areas
- 75% report that they are adding more residential subscribers than business subscribers
Services
- 66% offer in-house Wi-Fi services
- 6-25 Mbps services account for 60% of their business today
- 50% are offering less than 5 Mbps services today
- In 2017, about 50% of their customers subscribed at the lowest level; however, one year from now, they estimate that 25% of their customers will subscribe at the lowest level as they migrate to higher bandwidth services
Network Size
- The average number of subscribers per access point sector is predominantly from 11-30
- 80% have less than 5,000 total subscribers in their network; as subscriber growth continues, however, 60% plan to have less than 5,000 subscribers in three years
Customer Satisfaction
- 35% report that reliable connectivity is their customers’ main priority
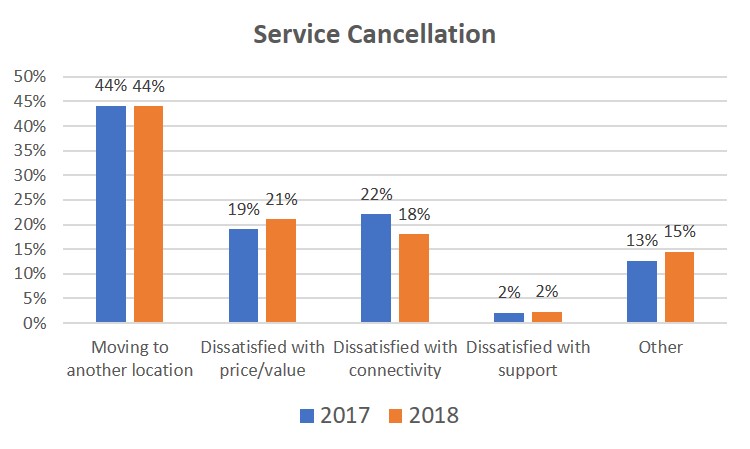
- 45% report that the main reason that customers cancel their service is because they are moving to another location
- 41% of their new business comes from referrals
WISP Business
- 30% report an annual revenue of less than $100,000
- 50% have fewer than five technical employees
- 60% have fewer than five non-technical employees
- The main information sources for WISPs are: communities and f, discussion with other WISPs, and discussion with resellers
The volume of responses and summary of those responses reflect a vibrant entrepreneurial industry that is expanding and evolving with the needs of its customer base. Technology and regulatory changes significantly influence the business: by example the FCC’s Citizens Broadband Radio Service supported by Shared Access Spectrum (SAS) services. Fixed LTE, advances in 802.11ay (60 GHz), and 24-29 GHz 5G solutions, will fuel the ongoing growth and capabilities of the industry.

