The World Economic Forum (WEF) has added 13 new smart factories to its ‘global lighthouse network’ of flagship sites for advanced manufacturing; its total network, proclaimed for their use of “Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies”, now stretches to 103 manufacturing facilities and “value chains”. Besides, three sites have been designated as ‘sustainability lighthouses’ for their “sustainability breakthroughs”.
The 13 new lighthouse factories include 10 in Asia and three in Europe; there are no new entries from the Americas or the Middle East, or indeed from Africa; the previous intake, a chort of 21, announced in September last year, included 13 factories in Asia, three in Europe, three in North America, and one in the Middle East. Of the total, more than half (53.4 percent) are in Asia, and most of those are in China, invariably. This compares with 35 percent in EMEA, and just 11.6 percent in the Americas.
The bi-annual intake is judged by the World Economic Forum and MckKinsey & Company; companies have to apply, first, in order to enter the review process to join the lighthouse list.
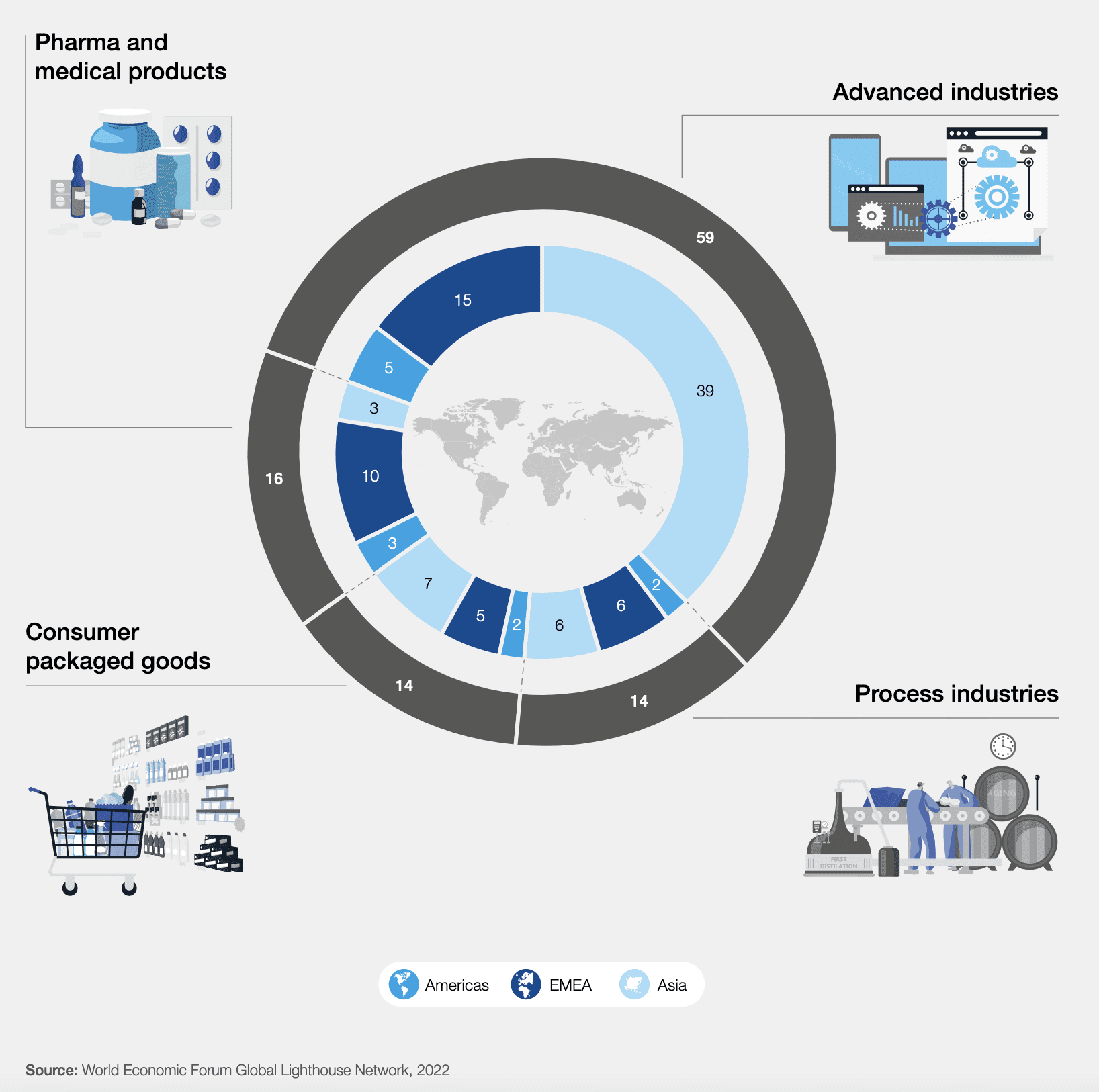
The World Economic Forum has divided the factory sites into four disciplines: advanced industries, process industries, pharmaceuticals and medical products, and consumer packaged goods. Most of the sites are categorized as advanced industries (59; 57.3 percent), with Asia over-indexing significantly (39; 66 percent); the rest are split fairly evenly between the remaining disciplines, and more evenly in each class between geographies (see graphic).
 There are a number of other takeaways from the latest report, to go with the latest intake, available here. The World Economic Forum (McKinsey & Co, handling the research and the maths) reckons 66 percent of lighthouse factories have made sustainability improvements by reducing consumption, resource waste, and carbon emissions, and 82 percent have increased their productivity. A full list of the 12 new entrants, copied directly, is included below. The three new sustainability lighthouses are linked here, as part of an list-review of the world’s most sustainable factories.
There are a number of other takeaways from the latest report, to go with the latest intake, available here. The World Economic Forum (McKinsey & Co, handling the research and the maths) reckons 66 percent of lighthouse factories have made sustainability improvements by reducing consumption, resource waste, and carbon emissions, and 82 percent have increased their productivity. A full list of the 12 new entrants, copied directly, is included below. The three new sustainability lighthouses are linked here, as part of an list-review of the world’s most sustainable factories.
Francisco Betti, head of advanced manufacturing at the World Economic Forum, said: “As the world grapples with many challenges, it is remarkable to see how lighthouses are yielding sustainability benefits while achieving business goals, which we call eco-efficiency. We need them to continue illuminating the way forward for the global manufacturing community by shaping a responsible future of manufacturing that works for people, society and the environment.”
Enno de Boer, partner global lead for digital manufacturing at McKinsey & Company, said: “The lighthouses show how digital technologies drive value chain resilience, growth, and environmental and people sustainability. In the past, sustainability and resilience have often come at the cost of efficiency, but that is no longer true. Companies now have a digital playbook and tech tools… to make their operations more flexible… and more sustainable… They can amplify human capability, achieve sustainability breakthroughs, and accelerate technological innovation – the recipe for smart manufacturing.”
Europe
The Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson (Latina, Italy)
Janssen Latina has been deploying Fourth Industrial Revolution solutions that deliver faster, competitive and agile launches of new products and quality release, led non-conformance reduction by 30% and product release lead time optimization by 84%, while reducing energy costs by 10% and logistics labour costs by 72%.
Sanofi (Paris, France)
With the ambition to accelerate saving generation, Sanofi embarked two years ago on a digital and analytics transformation of its procurement operations. To date, it has built and deployed six products – data platform, should-cost modelling and input-cost monitoring, smart tender analytics, supplier performance tracker and cockpit – that have delivered 10% savings on addressed spent and transformed the way of working.
Teva Pharmaceuticals (Amsterdam, Netherlands)
Global Procurement is the main contributor to Teva’s ambitious Gross Margin Improvement Program and contributes to the Free Cash Flow target, delivering three times historical Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) savings by the end of 2024. To achieve this, Global Procurement implemented Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies within 1.5 years, increased labour efficiency by 30%, upskilled its workforce and optimized cross-functional processes to break down silos. It is leading the way in Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies at Teva.
Asia
BOE Technology Group (Fuzhou, China)
To pursue premium product market share with high-quality expectation, BOE Fuzhou has widely adopted AI and advanced analytics in a fully automated production system to achieve best-in class quality excellence, equipment efficiency and energy sustainability with a new product yield ramp-up period shortened by 43%, cost per unit reduced by 34% and output increased by 30% without major capex investment.
Bosch Automotive (Changsha, China)
Facing a 20% labour wage increase, year-over-year 10%+ price reduction request from customer and high fluctuation in customer orders, Bosch Changsha implemented 45 Fourth Industrial Revolution use cases with automation and AI to increase competitiveness, maintained the market position with 100% NEV (new energy vehicle) customer portfolio penetration and reached carbon neutrality.
Haier (Zhengzhou, China)
Facing a booming market for water heaters and increasing requirements of high-end products and services, Haier Zhengzhou, leverages big data, 5G edge computing and ultra-wide band solutions to build a close connection with suppliers, plants and customers. This has sped up order response lead times by 25%, increased production efficiency by 31% and improved quality performance by 26% from 2020 to 2021.
Johnson & Johnson Consumer (Thailand) (Bangkok, Thailand)
Facing agility, profitability and cost to serve challenges, Johnson & Johnson Consumer Health site in Bangkok adopted Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies, such as collaborative supply chain control tower, computational fluid dynamics, AI energy optimization and advanced data analytics on logistics. The value chain delivers 47% revenue growth with 25% inventory reduction, and it reduced 43% end-to-end supply chain lead time, 42% productivity improvement and 20% carbon footprint optimization.
LG Electronics (Changwon, South Korea)
Facing growth of its product portfolio complexity by 70%, rising quality expectations from customers and labour shortages, LGE redesigned an old factory in Changwon, South Korea, into a digital plant leveraging flexible automation, digital performance management and AI to improve productivity by 17% and field quality by 70%, while reducing inventory by 30% and energy consumption by 30%.
Midea (Jingzhou, China)
Due to consumer expectations with higher product complexity, Midea Jingzhou, as a 30-year-old factory, adopted flexible automation, IoT and AI at scale to transform the manufacturing system, increase labour productivity by 52%, reduce production lead time by 25% and eliminate 20% utility consumption per unit.
Midea (Hefei, China)
Targeting domestic high-end product segments and oversea market expansion, Midea Hefei Laundry Appliances widely deployed AI and IoT technologies across end-to-end value chains to form a faster response and higher efficiency supply chain, which resulted in a lead time reduction by 56%, customer report defect rate reduction by 36% and labour productivity improvement by 45%.
Procter & Gamble (Guangzhou, China)
To meet 45% increased e-commerce demands, P&G Guangzhou leveraged AI, flexible automation and digital twins to integrate multi-systems across its value chain to serve omni-channel consumers. This increased the responsiveness of their supply chain with 30% reduction of inventory, 15% reduction of logistics cost and 99.9% on time delivery within three years.
Schneider Electric (Hyderabad, India)
Facing changing customer demands and a 54% business growth, Schneider Electric implemented Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies such as IIoT infrastructure, predictive/prescriptive analytics and AI deep learning. This has resulted in reduction of field failure by 48% and lead time by 67%, while manufacturing efficiency improved by 9%.
Unilever (Dapada, India)
Driven by the need to accelerate the pace of innovation and speed of response to consumer demand while augmenting cost competitiveness in an increasingly challenging market, and acting on sustainability goals, Unilever Dapada deployed digital, automation and AI-ML across its end-to-end value chain to shorten product development lead time by 50%, reduce manufacturing cost by 39% and energy by 31%.

