Global revenues from cellular IoT modules increased by 58 percent in the fourth quarter of 2021, compared with the year-ago period, with more than 40 percent of the total revenue in the period in China. 5G-based IoT modules contributed to nearly a quarter of the revenue figure, growing 324 percent on a year ago. Quectel, Telit, and MeiG remain the top three IoT module makers. The figures are from Counterpoint Technology Market Research.
India was the fastest growing regional market for IoT modules, said the research firm, with orders up by 154 percent in value. LTE-M (4G Cat 1) revenues were also significantly higher than the year-ago quarter, up by 105 percent year-on-year. Counterpoint listed the top applications for 5G-based IoT modules as automotive / vehicle connectivity, routers and CPE equipment, industrial equipment, personal computers, and point of sale (POS) equipment in retail.
Drones represent the fastest growing app-segment in value terms, followed by routers and CPE equipment; smart meters is “another key segment”, but registers lower in the revenue table on the grounds it exists at the lower end of the IoT market, attached to cheap NB-IoT and LTE-M modules. Qualcomm was the top cellular IoT chipset maker in the period, confirmed Counterpoint.
Quectel, Telit, and MeiG took 40 percent of IoT-module revenues in the quarter – although, as per the supplied graphic below, China-based Quectel took more than 25 percent on its own, making it completely dominant in the quarter.
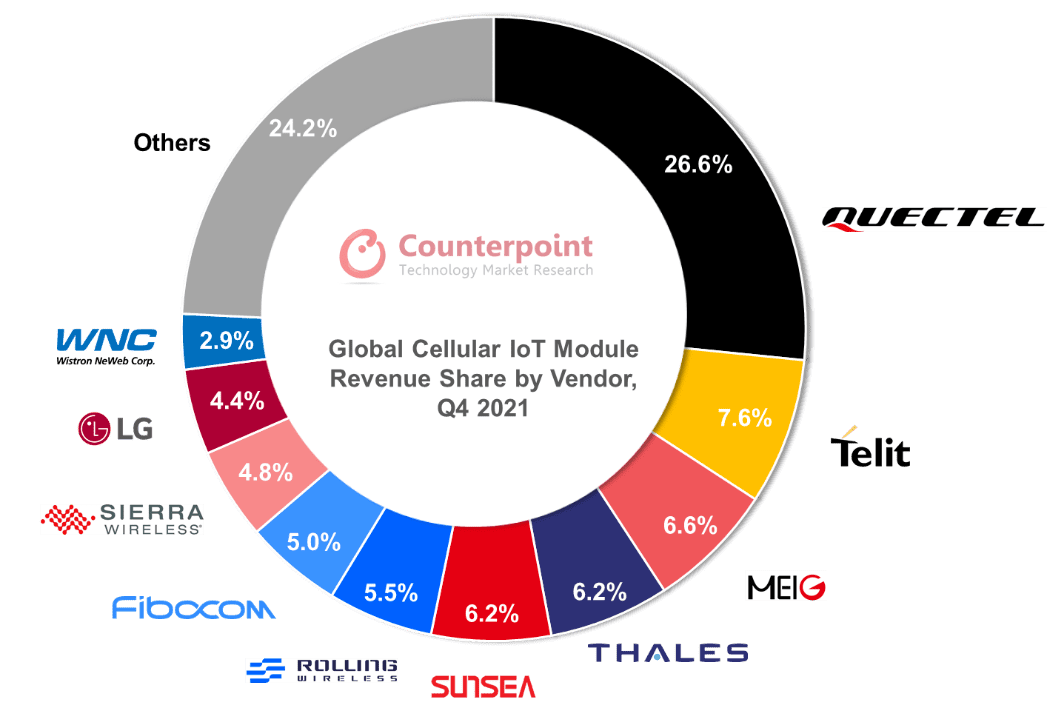
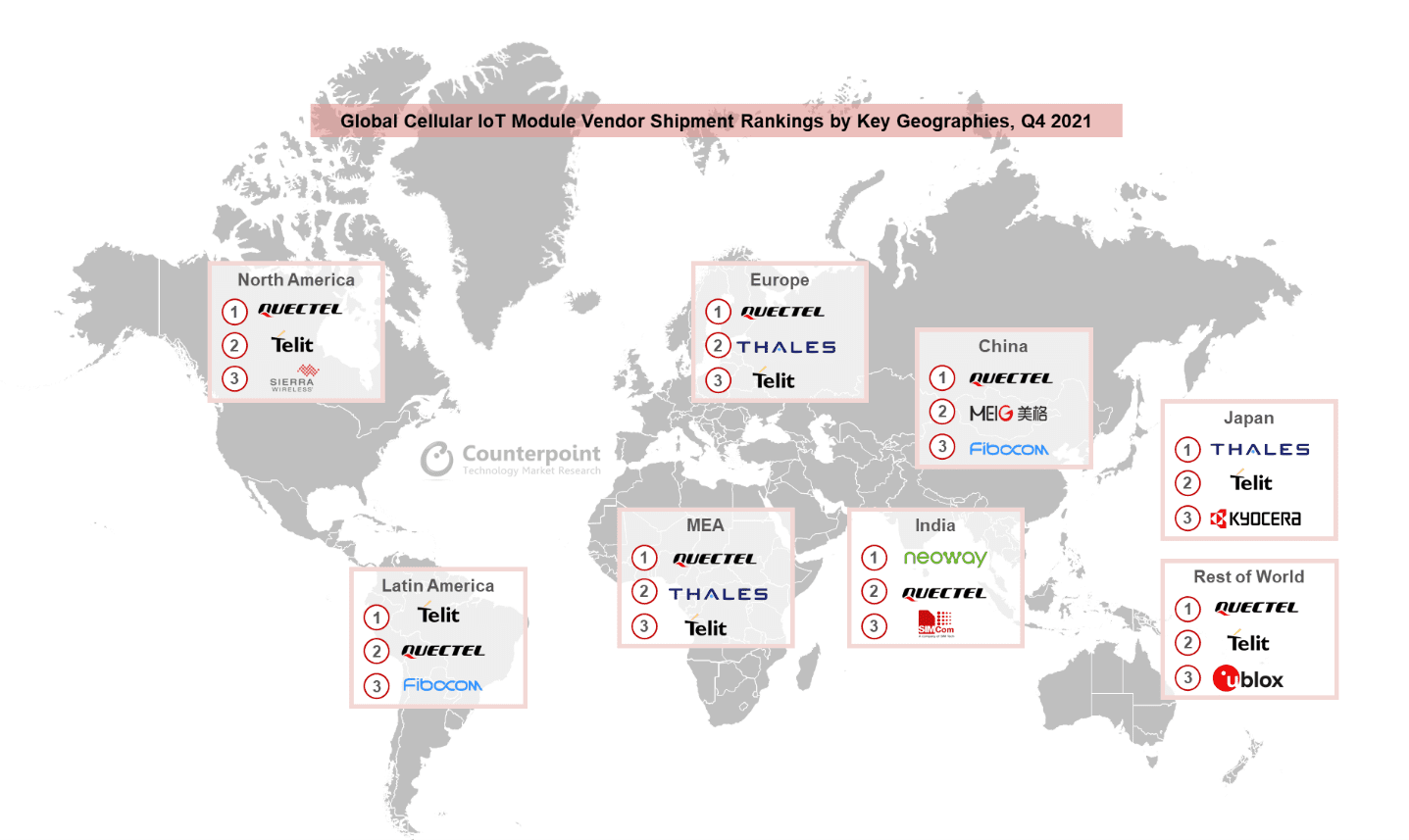
Quectel’s module revenues jumped by over 100 percent, based on “strong partnerships, superior service, and a wide range of product offerings”, said Counterpoint. “Quectel is leading in most regions except Latin America, India and Japan. However, as these regions currently represent a small share of the global cellular IoT module market, it doesn’t have much impact overall,” it said. “Japan’s preference for LTE-M works against Quectel,” it added.
Telit made a “strong comeback” in the quarter, after a “relatively weaker” recent performance. Counterpoint noted it has expanded its offerings, including with flexible connectivity – “to take advantage of emerging business models and remove bottlenecks for IoT device vendors”. Its focus on Latin America to migrate customers from 2G/3G modules to LTE-M has seen it take a “leading” position among module suppliers in the region.
Chinese brand MeiG, in third by shipment and revenue volumes, did well to mix higher- and lower-end modules, with revenues spiralling by more than 100 percent in the quarter. “In China, MeiG overtook Fibocom to become the second largest cellular IoT module vendor. Neoway, another Chinese module vendor, maintained its leading position in the Indian market [thanks to] strong partnerships with smart meter manufacturers and telematics providers,” it said.
Of the rest, Thales is “performing well” with meters, plus healthcare and industrial apps, in Europe, North America, and Japan, said Counterpoint. Meanwhile, Sunsea saw its revenue share go down in the period, even as its total revenues were up. Rolling Wireless and Sierra Wireless posted revenue jumps of 105 percent and 87 percent; the former was spun-out of the latter’s automotive division last year.
The average selling price of cellular IoT modules was seven percent higher quarter-on-quarter because of “supply-chain constraints”. Counterpoint said Chinese chipset players are trying to reduce the 5G prices for mass commercialisation. It stated: “However, 5G adoption hasn’t picked up as expected. We see 5G peaking in the global cellular IoT module market after 2025.”
Full-year shipment and revenue figures are in line, at 59 percent and 57 percent growth, respectively. Counterpoint has released a report with all the info; go here.
Neil Shah, vice president of research at Counterpoint, said, “International players made a strong comeback in Q4 2021 after weaker performance in the previous quarter. Quectel, MeiG and Sunsea were the top three cellular IoT module players in China in terms of revenue. For the rest of the world, Quectel, Telit and Thales were the top three cellular IoT module players.”

